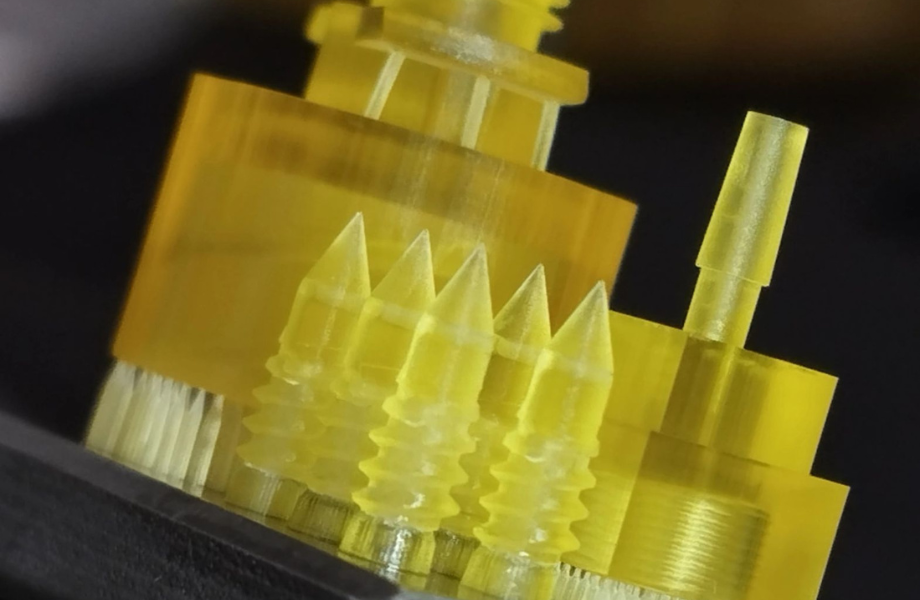
What is Projection Micro Stereolithography (PµSL)?
PµSL is a micro-scale 3D printing technology based on the principles of stereolithography (SLA). It uses a digital light projector to cure a photosensitive resin layer by layer, enabling the production of highly detailed parts with microscopic features. The key to its success lies in the projection of UV light through a digital micromirror device (DMD), allowing for extreme accuracy in patterning each layer of material. PµSL operates at submicron resolutions, making it suitable for manufacturing components that require fine detail and tight tolerances.
While conventional stereolithography (SLA) systems excel in producing larger parts, PµSL focuses on micron and sub-micron features, allowing the creation of parts as small as a grain of sand, with features invisible to the naked eye. This capability makes it a powerful tool for industries that need miniaturisation and high accuracy.
Pros of PµSL
Exceptional Accuracy
PµSL offers resolutions down to 2 µm, making it one of the most accurate additive manufacturing methods available for producing micro-structures.
Complex Geometries
This technology is ideal for producing parts with complex internal features and geometries that are difficult, if not impossible, to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
Material Flexibility
A wide range of materials, including polymers, ceramics, and composites, can be used in PµSL, depending on the application requirements. At Prototype Projects, we stock Matrix HTL and Matrix BIO.
Reduced Waste
Additive manufacturing by nature reduces waste compared to subtractive methods. PµSL is no exception, with its layer-by-layer process only using the necessary material for part creation.
Versatility
From medical devices to micro-optics and MEMS (microelectromechanical systems), PµSL is incredibly versatile, finding applications across a variety of fields.
Cons of PµSL
Limited Build Volume
One of the primary limitations of PµSL is its small build size, which makes it unsuitable for producing larger parts. It excels in creating small, detailed structures, but scaling up can be challenging.
Longer Production Times
The high resolution of PµSL, while beneficial for detail, can also result in longer build times compared to other 3D printing methods, especially when creating intricate parts with many layers.
Material Constraints
While PµSL supports a variety of materials, material properties may not always meet the demands of all industries, particularly when compared to traditional manufacturing techniques.
Cost
Due to the high-accuracy equipment required, PµSL can be more expensive than other additive manufacturing methods, especially for low-volume production.
Applications of PµSL
The unique capabilities of PµSL make it a critical technology for industries where accuracy and miniaturisation are vital. Below are some of the most common applications of this micro-scale technology:
Medical Devices
PµSL is widely used to create microfluidic devices, surgical tools, and other medical components that require high accuracy and complex geometries. Its ability to produce customised implants and biocompatible devices is also valuable in the healthcare industry.
Microelectronics and MEMS
The electronics industry benefits from PµSL’s ability to produce components for microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), which are essential for sensors, actuators, and micro-robotics. PµSL enables the fabrication of micro-scale parts that are critical in advanced electronics.
Optics and Photonics
PµSL is capable of producing micro-optical components, such as lenses and waveguides, with submicron resolution. These parts are crucial in fields like telecommunications, where light manipulation on a micro-scale is essential.
Microscale Prototyping
For design engineers working on microscale prototypes, PµSL offers an unparalleled solution for creating detailed, accurate models for testing and evaluation. The ability to prototype on a small scale with high accuracy can significantly speed up product development.
Microfluidics
PµSL is a powerful tool for fabricating microfluidic chips, which are used for applications ranging from medical diagnostics to chemical analysis. These devices require fine channels and intricate designs that PµSL can produce with ease.
Research and Development
Academic and industrial research teams benefit from PµSL’s ability to produce detailed microstructures for experimental purposes. Whether it’s investigating new materials or studying micro-scale phenomena, PµSL offers researchers the flexibility they need.
Conclusion
Projection Micro Stereolithography is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in 3D printing, providing a level of accuracy and complexity that was previously unattainable in microscale manufacturing. Although it comes with certain limitations, such as smaller build volumes and higher costs, its advantages in terms of accuracy, versatility, and material flexibility make it a key player in sectors like medical devices, microelectronics, and optics.
For design engineers, product designers, and mechanical engineers working on projects that require micro-level detail, PµSL opens new doors for innovation. As the technology continues to evolve, it’s likely we’ll see even broader applications, unlocking the potential for more industries to benefit from this cutting-edge technique.
Talk to us
To Learn more about Projection Micro Stereolithography - or any of our other 3D Printing, CNC Machining, Vacuum Casting and Model Making services, please contact us on 01763 249760.